
#T DM1 MECHANISM OF ACTION TRIAL#
Severe adverse events identified during the EMILIA trial included hepatotoxicity (liver damage), including rare cases of liver failure, hepatic encephalopathy, and nodular regenerative hyperplasia heart damage (dysfunction of the left ventricle) interstitial lung disease, including acute interstitial pneumonitis thrombocytopenia and peripheral neuropathy. Adverse effects ĭuring clinical trials, the most common adverse effects of trastuzumab emtansine were fatigue, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, thrombocytopenia (low platelet counts), headache, increased liver enzyme levels, and constipation. 6.4 months), along with improved overall survival (median 30.9 vs. This trial showed improved progression-free survival in patients treated with trastuzumab emtansine (median 9.6 vs.
#T DM1 MECHANISM OF ACTION PLUS#
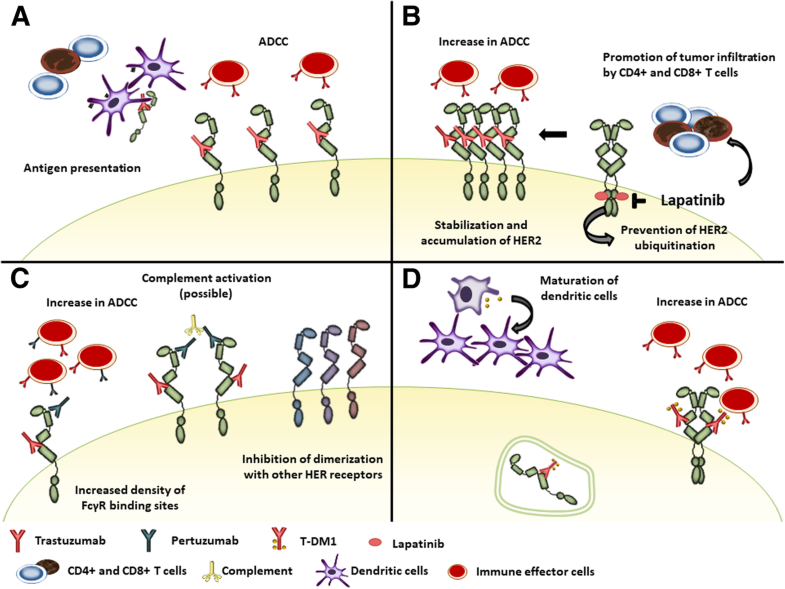
Īpproval was based on the EMILIA study, a phase III clinical trial that compared trastuzumab emtansine versus capecitabine (Xeloda) plus lapatinib (Tykerb) in 991 people with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer who had previously been treated with trastuzumab and taxane chemotherapy. In the United States, trastuzumab emtansine was approved specifically for treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (mBC) in patients who have been treated previously with trastuzumab and a taxane ( paclitaxel or docetaxel), and who have already been treated for mBC or developed tumor recurrence within six months of adjuvant therapy. Trastuzumab emtansine was developed by Genentech, and is manufactured by Lonza. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved marketing on 22 February 2013. 25.1 months) compared to the combination of lapatinib and capecitabine. In the EMILIA clinical trial of women with advanced HER2 positive breast cancer who were already resistant to trastuzumab alone, it improved median overall survival by 5.8 months (30.9 months vs. Because the monoclonal antibody targets HER2, and HER2 is only over-expressed in cancer cells, the conjugate delivers the cytotoxic agent DM1 specifically to tumor cells. Trastuzumab binding to HER2 prevents homodimerization or heterodimerization (HER2/HER3) of the receptor, ultimately inhibiting the activation of MAPK and PI3K/AKT cellular signalling pathways. Trastuzumab alone stops growth of cancer cells by binding to the HER2 receptor, whereas trastuzumab emtansine undergoes receptor-mediated internalization into cells, is catabolized in lysosomes where DM1-containing catabolites are released and subsequently bind tubulin to cause mitotic arrest and cell death. Trastuzumab emtansine, sold under the brand name Kadcyla, is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of the humanized monoclonal antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin) covalently linked to the cytotoxic agent DM1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
